Deep learning is at the forefront of Artificial Intelligence (AI), shaping how machines understand and interpret our world. This transformative technology mimics the human brain’s ability to recognize patterns and make informed decisions. But what is deep learning, how does it function, and where can it be applied? In this article, we’ll delve into these questions to help you grasp the essence of deep learning and its significance in today’s digital landscape.
As someone who has navigated the intricacies of AI, I understand that the journey from theory to application can be complex yet rewarding. Let’s explore the fascinating world of deep learning together.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of AI that utilizes multi-layered neural networks to learn from vast amounts of data. Imagine your brain identifying and learning distinct features of your surroundings; that’s how deep learning operates. It leverages interconnected nodes across multiple layers to process raw data, making strides in modern AI applications such as image recognition, language translation, and even chatbots.
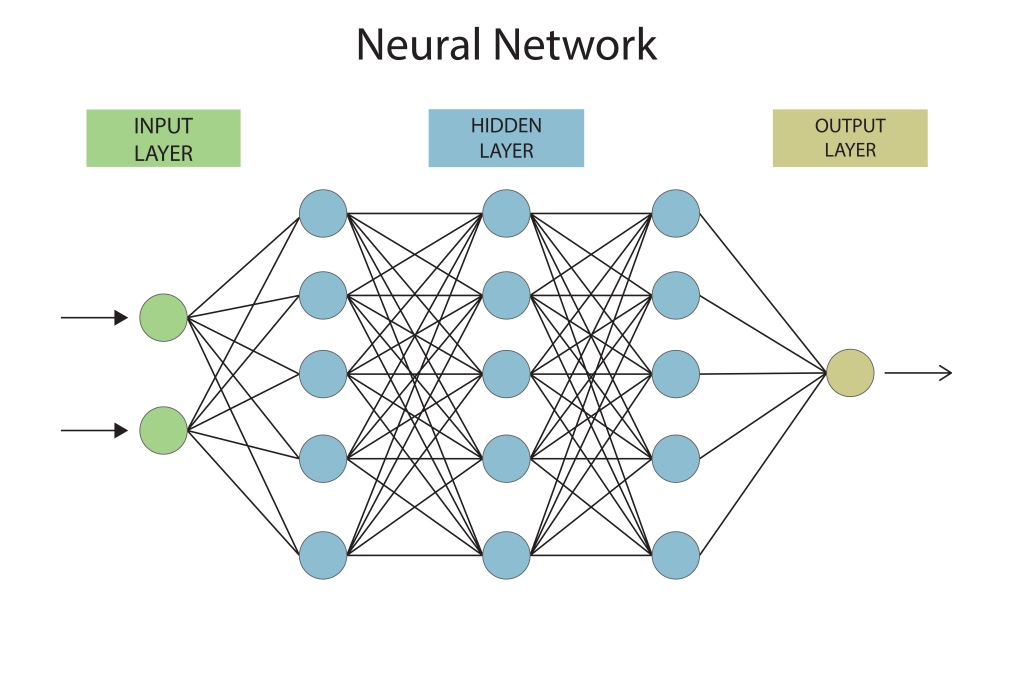
How Deep Learning Works
Understanding how deep learning processes information can feel complex, but let’s simplify it. Here’s a clear breakdown:
- Input Layer: This layer accepts raw data, such as images or texts.
- Forward Pass: The input data is processed through the network to generate predictions.
- Compute Loss: A loss function evaluates how accurate the prediction was.
- Backpropagation: The loss information is sent back to adjust the network’s parameters for better accuracy.
- Optimizer Step: The optimizer fine-tunes the parameters to minimize future errors.
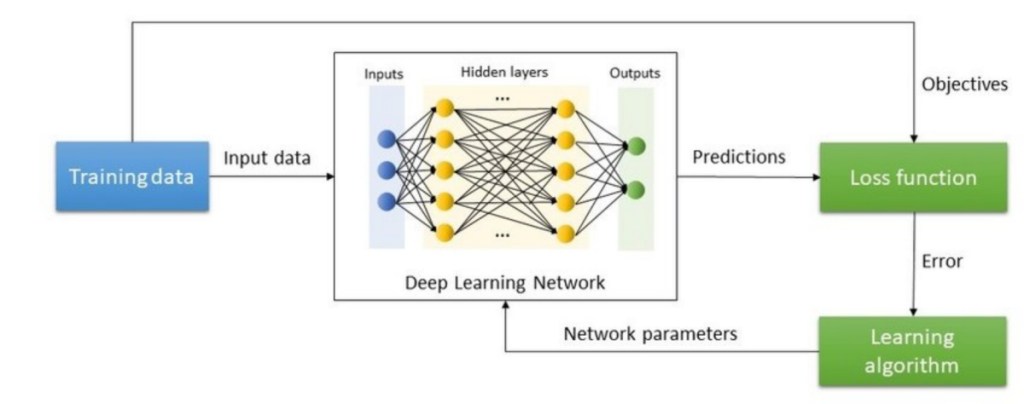
This cycle is repeated numerous times until the deep learning model achieves consistent accuracy in its predictions.
The Evolution of Deep Learning in AI
Deep learning may seem like a recent phenomenon, but its foundations trace back decades. Here’s a quick overview:
- AI Becomes a Research Field (1956): John McCarthy coins the term “artificial intelligence” during the Dartmouth Conference.
- Introduction of Neural Networks (1950s): Frank Rosenblatt creates the perceptron, the first single-layer neural network.
- Revival of Backpropagation (1986): Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun enhance training methods for multilayer networks.
- Modern Deep Learning Boom (2000s): Advances in technology lead to deeper networks that revolutionize image recognition.
- Transformers and Large Language Models (2017 onward): Google’s Transformer architecture signifies a major leap, influencing today’s AI systems.
Difference Between Deep Learning and Machine Learning
While deep learning is often confused with machine learning, understanding their differences is crucial. Here’s a simple comparison:
| Feature | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirements | Effective with small-to-moderate datasets, improves with more data | Excels with large datasets |
| Feature Extraction | Requires human programming for feature definition | Automatically learns patterns within the data |
| Model Type | Includes decision trees, SVMs, and ensemble methods | Utilizes Deep Neural Networks (CNNs, RNNs, Transformers) |
| Hardware | Primarily uses CPUs | Relies on GPUs and TPUs for optimal performance |
| Training Time | Generally quicker to train | Longer training periods and higher computational demands |
| Best Use Case | Structured or tabular data | Image, text, and speech recognition |
Types of Deep Learning Models
Curious about how deep learning models are categorized? Here are some widely recognized types:
1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs excel at processing images and videos, dividing them into grids for efficient processing. These networks recognize simple shapes at shallow layers and complex structures at deeper layers.
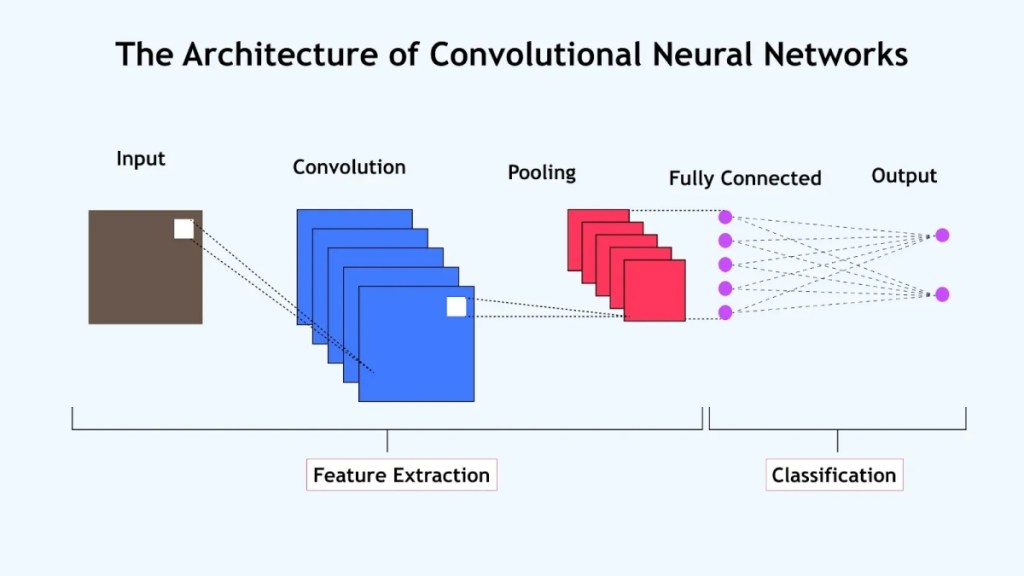
They’re essential for applications like image recognition and facial detection technologies.
2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs are perfect for handling sequential data, like text and speech, where order matters. They utilize loops to remember previous inputs, enhancing context comprehension.
3. Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM)
Addressing RNNs’ limitations, LSTMs utilize internal gates to manage information flow. They have proven effective in applications like speech recognition and music generation.
4. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs are a powerful tool for generating realistic data, such as images and music. They consist of two competing networks: a Generator and a Discriminator, which enhance each other’s capabilities.
5. Transformer Architecture (The Foundation of LLMs)
This architecture revolutionizes processing sequential data, featuring a mechanism called Self-Attention. It identifies the significance of different parts of the input data, making it invaluable for AI-driven applications.
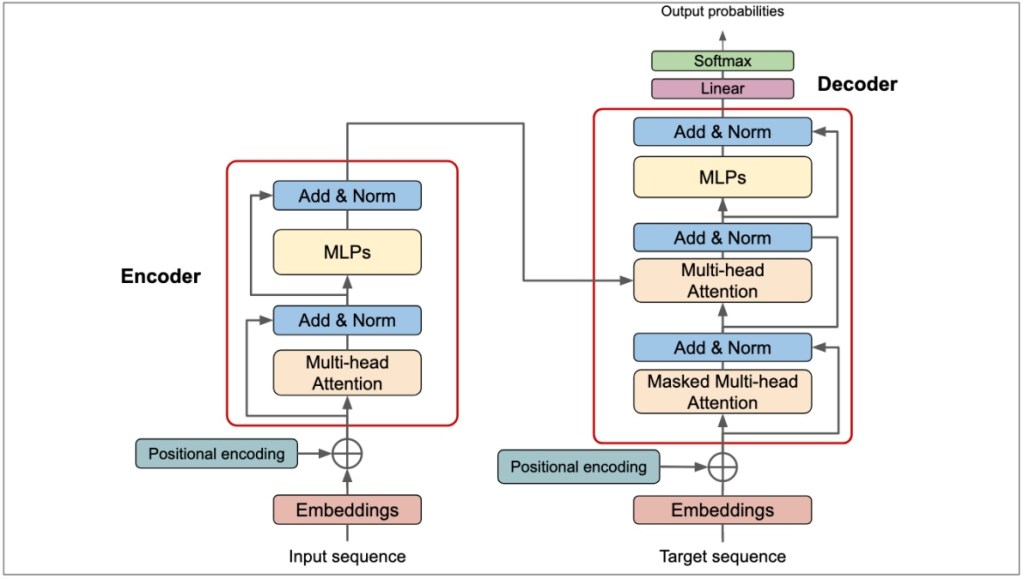
For example, when analyzing a sentence, the model identifies contextual words to discern meanings, facilitating applications like AI chatbots.
Applications of Deep Learning in AI
The prevalence of deep learning in various fields is astounding. Here are key applications you might encounter:
- Image Recognition
- Object Detection
- Facial and Fingerprint Scanning
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
- Text Summarization Tools
- Language Translation
- Music Generation
- Content Creation (Images and Videos)
- Personalized Advertising
- Medical Imaging Analysis (X-rays, MRIs)
These applications highlight how deep learning is reshaping industries everywhere. It’s fascinating that a concept originating in the 1950s is now part of daily innovations.
How does deep learning influence everyday technology? Deep learning powered by neural networks revolutionizes how we interact with machines, making them smarter and more intuitive.
Why is deep learning important for businesses? It enables companies to make data-driven decisions, enhancing efficiency and accuracy across various operations.
Can deep learning be used for small businesses as well? Absolutely! Even small organizations can leverage deep learning tools to improve customer engagement and optimize their operations.
What are the challenges faced when implementing deep learning? Organizations often encounter issues like high data requirements, training costs, and the need for specialized expertise.
As deep learning continues to evolve, so will its applications. I encourage you to stay curious and explore this dynamic field. For more insights and information about AI and its potential, consider checking out Moyens I/O.
